Type and hit Enter to search
Experts in aesthetic surgery, dermatology, and beauty bring you the latest trends, research, and advice to help you make informed decisions about your appearance and health.
A web platform dedicated to aesthetic surgery, dermatology, and beauty, where expertise meets innovation, and your desires and needs become our mission. In a world where appearance and health go hand in hand, our platform leads the revolution, delivering the latest trends, research, and expert advice directly to you.
Our team consists of highly skilled professionals in the fields of aesthetic surgery and dermatology, committed to providing reliable information and guidance that will help you make informed choices about your appearance and well-being. We understand that every individual has unique needs and desires, which is why we approach each person with the utmost care and professionalism.
Powered by Aestetica Web Design © 2024
Hair Cloning: Will We Soon Choose Hairstyles from a Catalog (and How Much Will It Cost)?
Baldness, that ancient enemy of human self-confidence, has plagued men and women around the world for centuries. Although it was once a sign of wisdom and maturity, today baldness is often seen as an aesthetic problem that can seriously damage self-esteem. But what actually causes hair loss and is there a magic wand that can restore lost hair? In this chapter, we'll dive deep into the world of baldness, debunking myths, exploring causes, and evaluating the effectiveness of various treatments.
Hair Loss 101: Understanding the Hair Growth Cycle
Did you know that we lose 50 to 100 hairs every day? This is a completely normal part of the hair life cycle. However, when you notice that your hair is falling out in larger amounts, that your scalp is thinning, or that you are developing bald spots, it’s time to worry. To distinguish normal hair loss from more serious problems, it is important to understand the phases of hair growth.
Each hair goes through three phases: anagen (growth phase), catagen (resting phase), and telogen (shedding phase). Under normal circumstances, about 85% of the hair is in the growth phase, while 15% is in the resting or shedding phase. However, various factors can disrupt this cycle and cause excessive hair loss.
Some of the most common causes of excessive hair loss include:
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress can “shock” hair follicles and cause them to prematurely enter the resting phase.
- Lack of nutrients: An unbalanced diet lacking in vitamins and minerals can weaken hair and make it more prone to falling out.
- Hormonal changes: Changes in hormone levels, such as those that occur during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid problems, can affect hair growth.
- Medical conditions: Certain diseases, such as alopecia areata or scalp infections, can cause hair loss.
- Medications: Some medications, such as chemotherapy or high blood pressure medications, can have the side effect of hair loss.
If you notice any unusual changes in the density or texture of your hair, it is important to consult a dermatologist or trichologist to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Genetics, Hormones, and Other Culprits: Why Does Our Hair Fail Us?
One of the most common causes of baldness, especially in men, is androgenetic alopecia, better known as male pattern baldness. This type of baldness is caused by a combination of genetics and hormones, specifically dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that is made from testosterone. DHT binds to receptors in hair follicles, causing them to shrink and shorten the hair life cycle.
Although genetics is the main risk factor for androgenetic alopecia, there are other factors that can contribute to hair loss. In women, hormonal changes during pregnancy, menopause, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can cause temporary or permanent hair thinning. Stress, iron deficiency, thyroid disease, and autoimmune diseases can also play a role in hair loss.
It is important to note that each case of baldness is unique and that the exact cause needs to be determined in order to determine the most effective treatment. Therefore, if you are concerned about hair loss, do not hesitate to seek professional help.
Marketing Magic or Miracle Cures? What Really Helps Against Baldness?
The market is flooded with products that promise lush hair and stop hair loss. From shampoos and lotions to pills and dietary supplements, the choice is huge. However, many of these products are based on dubious claims and lack scientific support.
Some of the most popular ingredients in hair loss products include minoxidil, finasteride, biotin, saw palmetto, and caffeine. Although some studies suggest that these ingredients may have some effect on hair growth, the results are often modest and temporary.
Minoxidil, for example, can stimulate hair growth in some people, but its effectiveness varies depending on individual factors. Finasteride, a drug used to treat enlarged prostate, can slow hair loss in men, but it can also have side effects such as decreased libido and erectile dysfunction.
Biotin, a B vitamin, is often touted as a “hair vitamin,” but there is not enough evidence to support claims that it can prevent hair loss or promote hair growth. Saw palmetto, an herbal extract, is also often used in hair loss products, but its effectiveness has not been scientifically proven.
In short, although some hair loss products may have some effect, it is important to be realistic in your expectations and consult with an expert before spending money on expensive treatments that may not give the desired results.
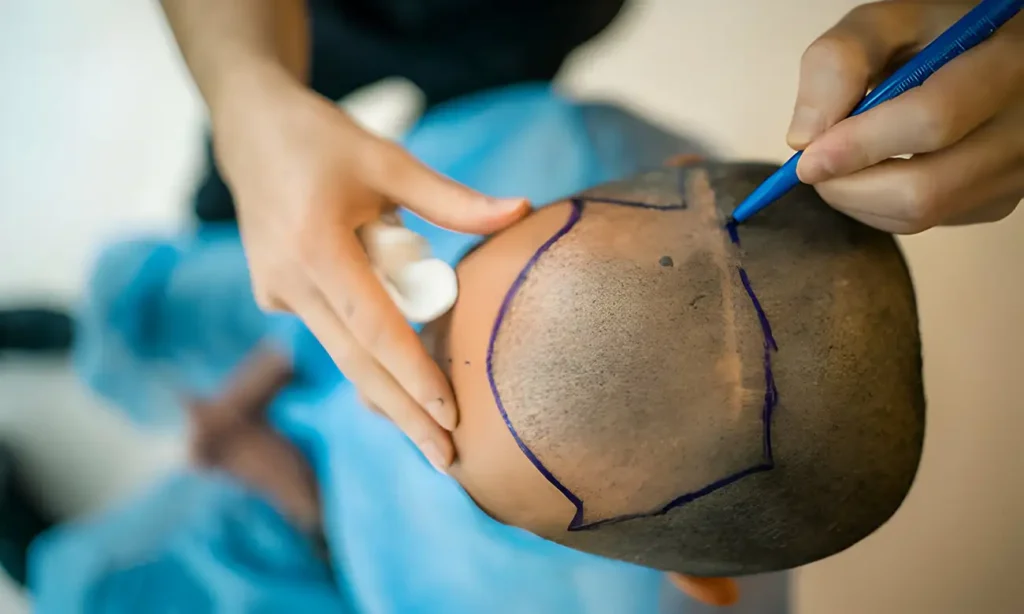
Hair Transplantation: Why It’s (Still) the Best Solution (for Those Who Can Afford It)
For those seeking a more permanent solution to baldness, hair transplantation may be the best option. This surgical procedure involves transplanting hair follicles from one part of the scalp (donor area) to another part of the scalp (recipient area).
There are two main methods of hair transplantation: FUT (follicular unit transplantation) and FUE (follicular unit extraction). The FUT method involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area, which is then divided into smaller follicular unit grafts. The FUE method involves individually extracting hair follicles from the donor area using a special tool.
Hair transplantation can be very successful in restoring lost hair, but it is not without risks and disadvantages. Recovery from the procedure can be lengthy, and complications such as infection, scarring, and unnatural hair appearance are possible. In addition, hair transplantation is an expensive procedure that is not available to everyone.
However, despite the high cost and potential risks, hair transplantation remains the most effective method for hair restoration.
Forget the myths about magic potions and dubious treatments. Hair cloning, once reserved for science fiction movies, has become a hot topic in the world of science and aesthetic medicine. But what is behind this intriguing term? Is hair cloning a magic wand that will solve the problem of baldness forever or just another passing fad? In this chapter, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of hair cloning, uncovering the secrets of hair follicles, exploring laboratory methods, and considering the potential applications of this revolutionary technology.
Hair Follicles: Tiny but Powerful Creators of Our Hair
Hair follicles, those tiny but incredibly important organs, are responsible for the growth and development of our hair. Located deep in the skin, hair follicles contain stem cells that divide and differentiate, creating new hairs. Each hair follicle has its own life cycle, which consists of three phases:
- Anagen phase (growth phase): In this phase, the cells in the follicle divide rapidly, producing new hair. Hair grows about 1 cm per month during this phase, which can last from two to six years.
- Catagen phase (resting phase): After the anagen phase, the follicle enters a short resting phase, during which hair growth stops. This phase lasts about two weeks.
- Telogen phase (shedding phase): In this phase, the old hair falls out and the follicle prepares for a new growth cycle. The telogen phase lasts about three months.
Normally, about 85% of hair follicles are in the growth phase, while 15% are in the resting or shedding phase. However, with baldness, this cycle is disrupted, leading to a decrease in the number of active follicles and thinning hair.
Hair cloning is based on the idea that new, healthy hair follicles can be created to replace those that have stopped functioning. This would allow hair regrowth and solve the problem of baldness permanently.
Laboratory Wizards: How is Hair Cloned?
The process of hair cloning begins by taking a sample of hair follicles from the patient’s scalp. These follicles are then transferred to the laboratory, where the stem cells responsible for hair growth are isolated.
The stem cells are then placed in special conditions that encourage them to divide and multiply. After a sufficient number of cells are created, they differentiate into different types of cells that make up the hair follicle.
Finally, the newly created hair follicles are transplanted back onto the patient’s scalp, where they are expected to take root and start producing new hair.
Although this process sounds simple, hair cloning is actually a very complex technology that requires precision and expertise. One of the biggest challenges is ensuring that the cloned hair looks natural and does not differ from existing hair.
From Test Tube to Scalp: Transplantation of Cloned Hair
The transplantation of cloned hair is similar to traditional hair transplantation, but with one key difference: instead of transplanting existing hair follicles, newly created follicles that were grown in the laboratory are transplanted.
This procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia and takes several hours. After the transplant, the patient may experience mild discomfort and swelling, but most people recover quickly and can return to their daily activities within a few days.
One of the main advantages of hair cloning over traditional transplantation is that it does not require a large number of existing hair follicles. This means that this method is also suitable for people with advanced baldness, who do not have enough healthy follicles for transplantation.
Hair of the Future: What Else Can We Expect from Hair Cloning?
Hair cloning has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of baldness, but its application does not have to be limited to that. Scientists are exploring the possibility of using cloned hair to treat burns, scars, and other conditions that cause hair loss.
In addition, hair cloning could be used to create new organs and tissues. Stem cells from hair follicles have the ability to differentiate into different types of cells, making them a potential source for regenerative medicine.
Of course, like any new technology, hair cloning raises many ethical questions. Should we allow hair cloning for aesthetic purposes? What are the
limits of this technology and how can we ensure that it is used responsibly? These questions are important to discuss as hair cloning continues to develop and become more accessible.
Hair Cloning: Myth or Reality?
Hair cloning, it seems, promises a miraculous solution for all those who struggle with hair loss. But is this technology really ready for “prime time” or is it still in the realm of science fiction? Is hair cloning a reality that will allow us to say goodbye to baldness or just another myth that will fade away like morning fog? In this chapter, we’ll come down from the clouds of promise to the ground of reality, exploring the current state of research, comparing hair cloning with other treatments, estimating costs, and considering the potential implications of this revolutionary technology.
Hair Cloning Today: Where Are We and What Can We Expect?
Hair cloning is not yet a standard procedure in clinics around the world. Although scientists have made significant progress in understanding the biology of hair follicles and developing methods for their multiplication, there are still many challenges to overcome.
Currently, several companies and research teams around the world are actively working on the development of hair cloning technology. Some of the most well-known include HairClone (United Kingdom), Aderans Research Institute (Japan), and Histogen (USA). These companies are conducting clinical trials to test the safety and efficacy of their hair cloning methods.
While preliminary results are promising, it is still too early to say when hair cloning will become widely available. Experts estimate that this technology could become commercially available in 5 to 10 years, but this depends on the success of clinical trials and regulatory approval.
Hair Cloning vs. Other Treatments: Who Will Win the Battle Against Baldness?
Compared to other baldness treatments, hair cloning has several potential advantages. Unlike drugs like minoxidil and finasteride, which only slow hair loss and can have side effects, hair cloning promises a permanent solution to the problem.
Also, unlike hair transplantation, which is limited by the number of available hair follicles, hair cloning allows the creation of an unlimited number of new follicles. This means that this method could be effective even for people with advanced baldness.
However, hair cloning also has its drawbacks. This technology is still under development and its long-term safety and efficacy have not been fully elucidated. In addition, hair cloning is likely to be an expensive procedure, at least initially, making it inaccessible to many people.
The Price of Beauty: How Much Will Hair Cloning Cost?
Given that hair cloning is still in the experimental phase, it is difficult to accurately estimate how much this procedure will cost when it becomes commercially available. However, experts estimate that the price could be significantly higher than the price of traditional hair transplantation, which ranges from several thousand to several tens of thousands of euros.
The price of hair cloning will depend on several factors, including the number of hair follicles that need to be cloned, the complexity of the procedure, and the reputation of the clinic. Also, the price could vary depending on the country where the procedure is performed.
Although the high price is currently one of the main obstacles to the wider application of hair cloning, the costs are expected to decrease as the technology develops and becomes more accessible.
Dream Hair: Will We Be Able to Choose a Hairstyle from a Catalog?
One of the most intriguing possibilities of hair cloning is the personalization of appearance. Scientists believe that in the future they may be able to manipulate the genes of hair follicles to create hair of the desired color, texture, and density.
This would mean that we could choose a hairstyle from a catalog, just as we choose clothes or makeup today. Want thick, curly hair like an 80s diva? Or maybe straight, silky hair like a Hollywood star? With hair cloning, anything is possible.
Of course, this idea also raises many ethical questions. Should we allow people to change their appearance in such a drastic way? Will this lead to new forms of discrimination and pressure to conform to certain standards of beauty? These are important questions to discuss as hair cloning continues to develop and become more accessible.
Biography of Dr. Gorana Kuka Epstein
Dr. Gorana Kuka Epstein is a specialist in plastic and aesthetic surgery. She is a professor at the Miami University School of Medicine, a diplomate of the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery, and a doctoral candidate at the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Novi Sad. Dr. Kuka Epstein is the founder and director of the FoundHair Training program, the founder of the Center for the Treatment of Female Hair Loss, the director of the research department at the Foundation for Hair Restoration in Miami, and the founder of the Dr. Gorana Kuka Foundation.
Reference